disc stack centrifuge Supplier & manufacturers | Shenzhou
The disc-stack centrifuge is the most common centrifuge used for separating algae biomass for various applications including algal biodiesel in pilot plants.. It consists of a shallow cylindrical bowl spaced between metal discs and is suitable for separating particles with the size of 3–30 μm with very low concentrations of 0.02%–0.05% of microalgae cultures up to 15% solid
A disc-stack centrifuge has been used successfully not only to separate solids/liquids, but also liquids/liquids from each other by using very high centrifugal forces in a single continuous process ]. This type of centrifuge has a very low separation time as a result of its ability to apply a centrifugal force 4000–14,000 times gravitational force. The more dense solid particles that are subjected to such high centrifugal forces are forced outwards against the wall of the rotating bowl, while less dense liquid particles are displaced in the center. Materials of various densities are, thus, separated into thin layers, and the narrow flow channel by 0. 4–3 mm between the closely-spaced discs implies that the distance materials must travel for this separation to occur is small . Disc-stack centrifuges come in several types based on the mechanism of discharge and whether the solids are discharged or retained.
The main drawback of the disc-stack centrifuge is that it exhibits higher energy consumption than the other types. Amaro et al. [118] studied the energy consumption of Westfalia HSB400 disc-bowl centrifuge with a limited flow rate of 35 m3/h and an approximate normal operating demand of 50 kW. Based on these specifications, the separation energy cost can reach up to 1.43 kWh/m3. In order to conduct an economic analysis for biodiesel from algae using the Westfalia HSB400, a set of assumptions was made. The disc-stack centrifuge is fed with 0.02% of the dry weight of microalgae suspension having an oil content of 40%. This would produce 7 kg/h of dry algal material, thus, 1.6 kg of algal oil. Assuming the recovery efficiency of the centrifuge is 100%, the 1.6 kg of algal oil obtained would yield an energy density of 11.71 kWh if the calorific value is assumed to be 7.32 kWh/kg . Considering a 35 m3 of culture broth required to be centrifuged to obtain such an energy yield, corresponding energy consumption of 49 kWh is needed. This means that the energy consumed at the harvesting-dewatering step only is 4 times the energy produced from microalgae as biodiesel.
To improve the energy return by centrifugation, pre-concentration by separation techniques to 0.5% of the dry weight is recommended. This would result in a dry algal material of 175 kg yielding 70 kg of algal oil, thus, 70 kg of algal biodiesel having a calorific value of 512.4 kWh. In this case, 9.6% of the energy in the biodiesel product would still be required to cover the energy consumption of centrifugation. Other recommended steps to improve energy efficiency include the use of the entire biomass instead of just the lipid fraction for energy production, or the use of centrifuges to remove other energy-intensive unit operations in the production of algal biofuels [118].
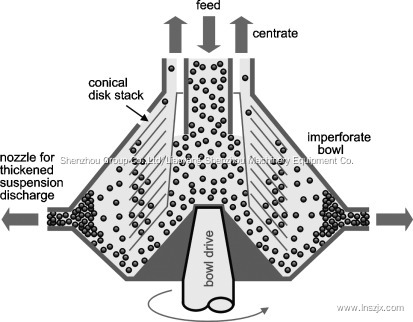
Cell disruption and damage can occur due to the use of disc-stack centrifuges as it was reported by Milledge et al. [120]. This also can be coupled with a reduction in the overall efficiency of centrifugation and a reduced concentration of solids recovered as a result of the smaller solid particles. Based on the parameters of a disc stack manufacturer (Fig. 7) [120], a minimum size of 7 μm for micro-eddies has been found to be suitable for microalgae. Hence, extensive further researches to modify the design of the disc-stack centrifuges is highly recommended.
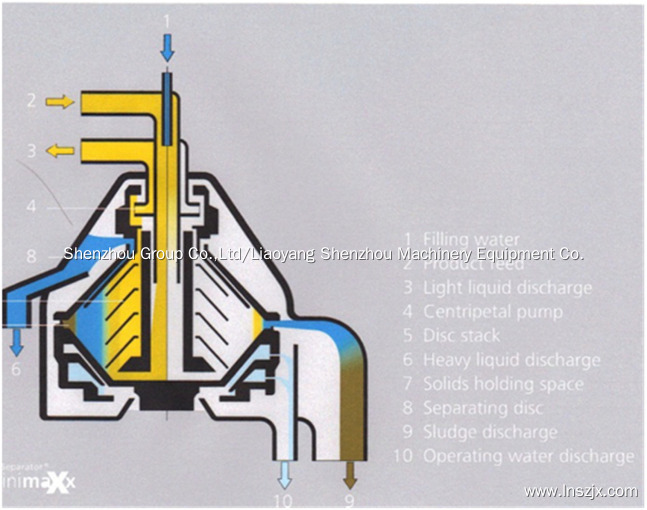
The disc stack centrifuge is a versatile device, which may be used for separating solid/liquid mixtures in continuous, semi-continuous and batch configurations (see Figures 1.12 and 1.13). All except some batch-operated machines are able to handle toxic, flammable and volatile feeds at throughputs up to 200 m3 h−1. Liquid-liquid mixtures can be separated and with more sophisticated units a three (two liquid and one solid) phase separation is achievable. In all cases, a sufficient density difference must exist between the phases present in the feed.