Application of Decanter Centrifuges in the Mining Industry
# Decanter Centrifuges: Core Solid-Liquid Separation Equipment in the Mining Industry
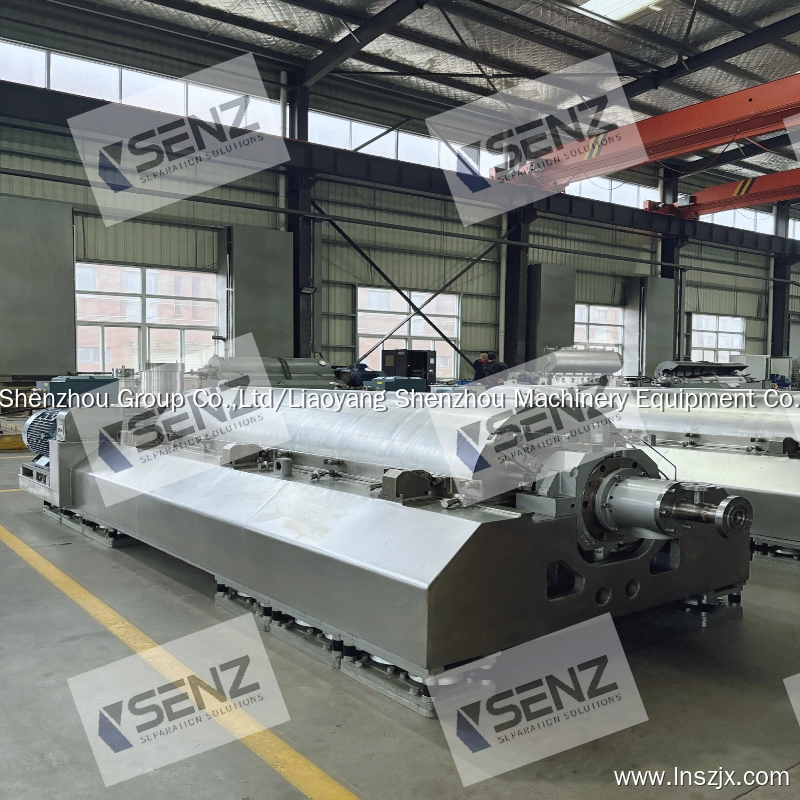
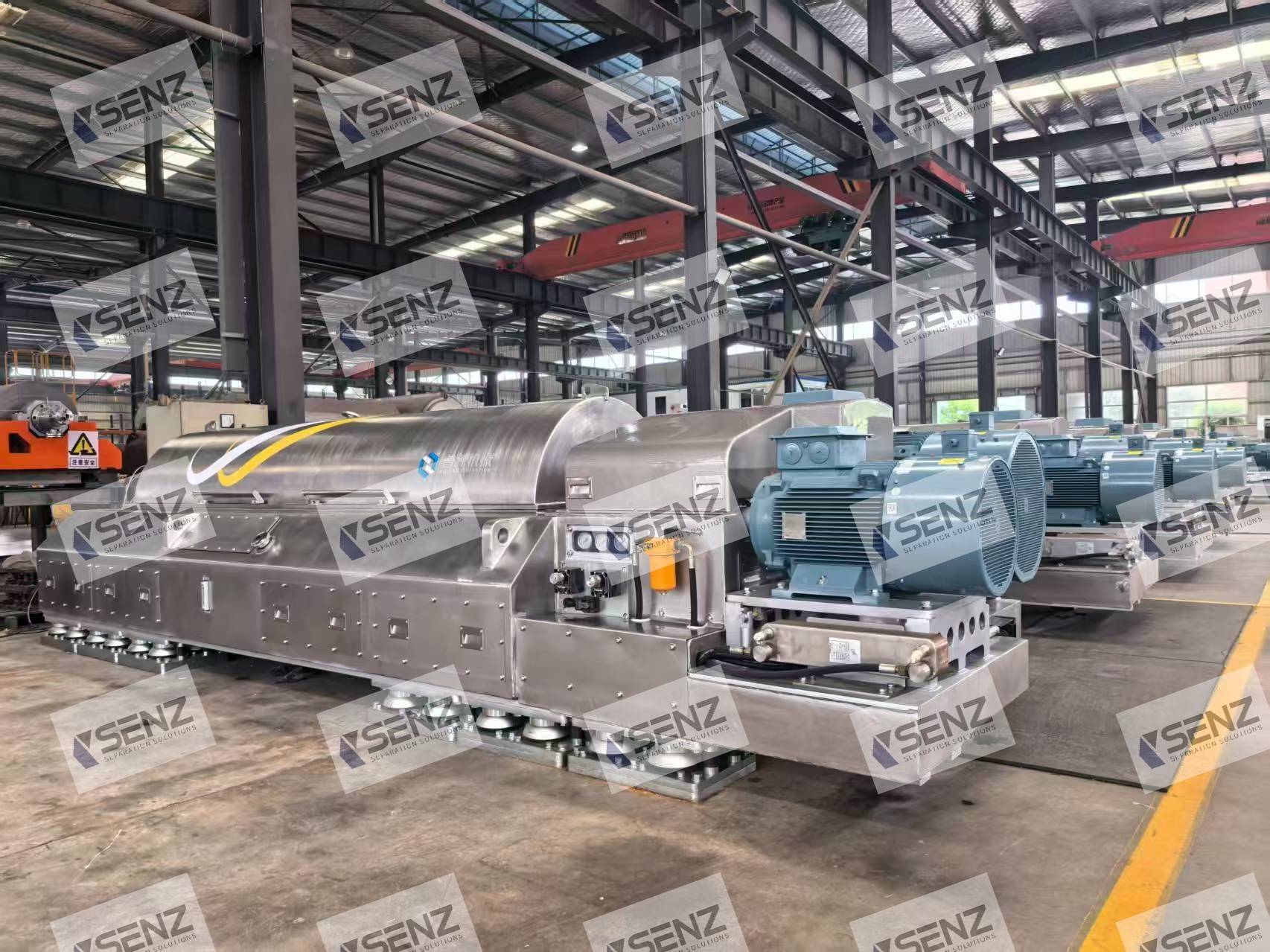
Decanter centrifuges are the **core solid-liquid separation equipment** in the mining industry. They are mainly used in critical processes such as mineral slurry dewatering, tailings treatment, and wastewater reuse. These centrifuges efficiently separate minerals from water/reagents, balancing production efficiency with environmental compliance, and are suitable for various mining scenarios.
## Core Application Scenarios
### 1. Mineral Slurry Dewatering and Separation
It processes mineral slurries after flotation and gravity separation to separate solid minerals from reagent-containing aqueous solutions. For example:
- In the coal industry, it dewaters clean coal/tailings coal.
- In metal mines (copper, iron, lead-zinc mines), it dewaters concentrates.
The result is solid minerals with low moisture content (facilitating transportation and subsequent processing), while the aqueous solution is recycled for reuse.
### 2. Tailings Dry Stacking Treatment
For mining tailings (waste slag slurry after mineral processing), solid-liquid separation is achieved through centrifugal force:
- The moisture content of tailings slag can be reduced to **20%-30%**, forming dry-stacked tailings. This reduces the land occupation of tailings ponds and lowers the risk of dam failure.
- The separated clean water can be reused in mineral processing processes, saving water resources.
### 3. Mining Wastewater Purification
It treats mining wastewater and mineral processing wastewater (containing suspended solids, heavy metal ions, and mineral processing reagents):
- Removes solid particles and some pollutants from water.
- Enables wastewater to meet either the standards for recycling (e.g., make-up water for mineral processing) or discharge, preventing pollution to soil and water sources.
### 4. Heavy Medium Recovery
In the coal heavy-medium separation process, it recovers heavy media (e.g., magnetite powder) from mineral slurries:
- Reduces heavy medium loss and lowers mineral processing costs.
- Simultaneously purifies coal preparation wastewater.
### 5. Mineral Classification and Purification
For fine-grained minerals (particle size: **2-50μm**), it achieves coarse-fine particle classification by adjusting centrifugal parameters:
- Enriches target minerals and improves the efficiency of subsequent mineral processing.
- Typical applications include the classification and purification of quartz sand and kaolin in non-metallic mines.
## Core Advantages in Applications
### 1. Efficient Continuous Operation
- Processing capacity ranges from **10-100 m³/h**, suitable for large-scale mining production.
- No shutdown is required for slag discharge, significantly improving mineral slurry processing efficiency.
### 2. Wear and Corrosion Resistance
- Wetted parts are made of wear-resistant alloys (e.g., duplex steel, Hastelloy) or rubber linings.
- Resistant to erosion from high-hardness mining slurries (containing wear-resistant particles like quartz sand) and acidic/alkaline mineral processing reagents, ensuring a long service life.
### 3. Water Conservation and Environmental Friendliness
- Water resource recovery rate after separation exceeds **80%**, reducing fresh water consumption in mines.
- Dry stacking of tailings reduces environmental pressure, aligning with the requirements for "green mine" construction.
### 4. Strong Adaptability
- Capable of handling slurries with high solid content (**5%-40%**) and high viscosity (**≤200 mPa·s**).
- By adjusting rotational speed (**2000-4500 rpm**) and differential speed (**3-20 rpm**), it adapts to the processing needs of different mineral types, including coal, metal ores, and non-metallic ores.
## Typical Application Cases by Mineral Type
### 1. Coal Industry
A large coal preparation plant of a coal mine adopted **LW series decanter centrifuges** to process tailings slurry after heavy-medium coal separation:
- Processing capacity: 30 m³/h.
- Moisture content of tailings coal reduced from 75% to 25%.
- Magnetite powder recovery rate reached 98%.
- Annual savings in heavy medium procurement costs exceeded 2 million RMB.
- All wastewater was reused in coal preparation, saving 120,000 tons of water annually.
### 2. Copper Mines
A copper mine in Jiangxi Province used decanter centrifuges for dry stacking of flotation tailings:
- Solid content of tailings slurry: 25%.
- Moisture content of tailings after treatment: 28%.
- Land occupation for dry stacking was only 1/3 of that of traditional tailings ponds.
- COD removal rate of separated wastewater reached 60%, meeting the standards for recycled mineral processing and reducing pollution to surrounding rivers.
### 3. Quartz Sand Mines
A quartz sand processing plant in Anhui Province used decanter centrifuges for fine-grain classification:
- Separated impurity particles with particle size ≤10 μm.
- Purity of quartz sand increased from 98.5% to 99.9%.
- Classification efficiency was 40% higher than that of traditional spiral classifiers.
- Suitable for the production needs of high-end glass and electronic-grade quartz sand.
### 4. Iron Ore Industry
An iron mine in Hebei Province used decanter centrifuges to process iron concentrate slurry after magnetic separation:
- Moisture content of concentrate reduced from 35% to 18%, facilitating subsequent sintering and pelletizing.
- Simultaneously recovered flotation reagent solutions from the slurry; reagent consumption decreased by 30% after recycling.
## Key Technical Adaptation Points
### 1. Material Selection
- For high-hardness slurries (e.g., coal, quartz sand): Wetted parts use **wear-resistant alloy + rubber linings**.
- For slurries containing acidic reagents (e.g., copper ores, pyrite): **316L stainless steel or Hastelloy** is selected.
### 2. Parameter Adjustment
- Rotational speed adjustment: Choose **2000-3000 rpm** for coarse-grained slurries and **3000-4500 rpm** for fine-grained slurries.
- Differential speed is controlled at **3-20 rpm** to balance separation efficiency and solid recovery rate.
### 3. Process Matching
- Often used in combination with thickeners (for pre-concentration) and filter presses (for deep dewatering), forming a process chain of "**pre-concentration - centrifugal separation - deep dewatering**".
- Example: Tailings are first concentrated to 30% solid content by a thickener, then separated by a decanter centrifuge, and finally dewatered to a moisture content of ≤15% by a filter press.
 |  |